
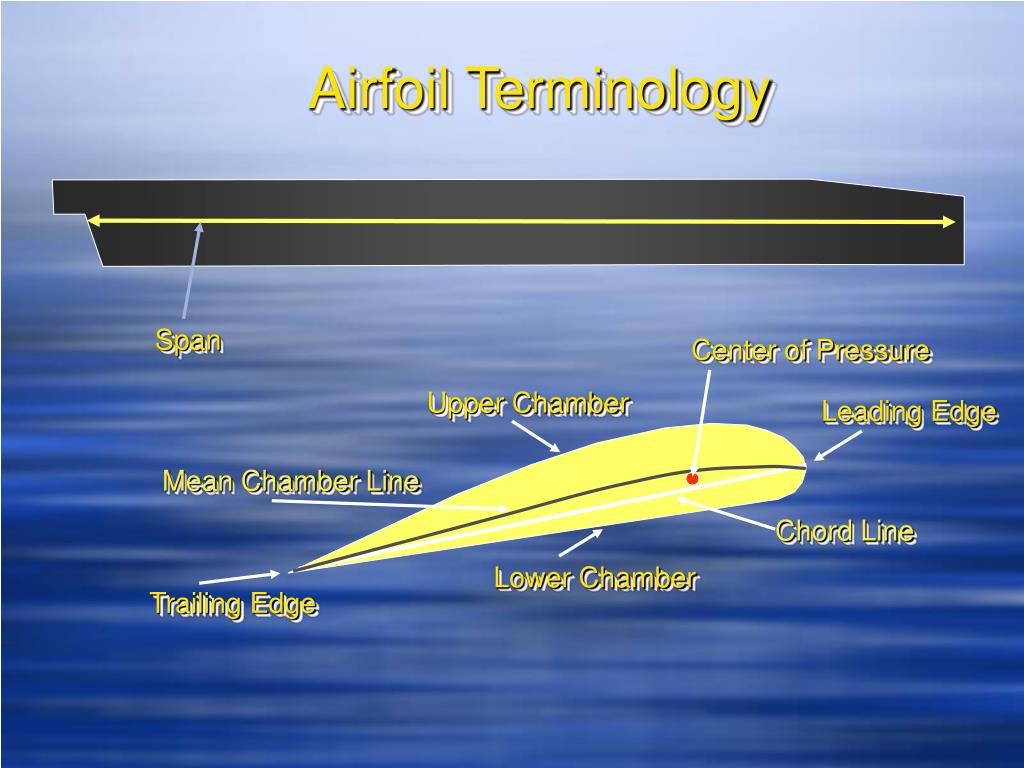
If we draw an imaginary line from the leading edge to the trailing edge of the wing, this line is referred to as the chord line. First, we’ll take a look at one of our archer wings and we see from the wingtip here, we can create a cross-section of what the wing would look like.
To get us started, I want to go over some basic terminology so that we can all be on the same page with some of the vocabulary that I’m going to use. So, we’re going to talk a little bit about the aerodynamics involved in how a wing produces lift to start with, and ultimately then, how it would stall and dramatically reduce the amount of lift that it produces. Maybe not stop but produce significantly less lift. We’re referring to an airfoil stall, which means an airfoil, such as the wing, is going to stop producing lift. In the case of airplanes, this is a little bit different. Specifically, their car engine stalling out and then therefore not producing any power. Most people, when they hear the term stall, they typically infer their car.

I want to make sure that we’re clear as to what that means. Today we’re going to talk a little bit about airfoil stalls. Power requirements are estimated at 0.22% of the AEP of the machine, while fatigue and ultimate load reduction of the flap-wise bending moment at the blade root is 27.6% and 7.4%, respectively.Airfoils, Stalls and Critical Angle of Attack – Video Transcript The results prove the potential of the concept, since the SMA controlled actuators can accurately follow the target trajectories. Numerical simulations are performed considering various wind velocities and morphing target shapes and trajectories for both normal and extreme turbulence conditions. The concept is embedded in the trailing edge region of the blade of a 10-MW horizontal axis wind turbine and acts as a flap mechanism. Shape memory alloy (SMA) actuators are investigated and assessed as means to control the shape adaptive mechanism at airfoil section level in order to alleviate the developed structural loads. Turbine scale level, a shape adaptive concept that encompasses an articulated mechanism consisting of two subparts is presented. Based on aeroelastic simulations that prove the enhanced capabilities of combined individual pitch and individual flap control at global wind Upscaling of wind turbine blades calls for implementation of innovative active load control concepts that will facilitate the flawless operation of the machine and reduce the fatigue and ultimate loads that hinder its service life. These results are fundamental for choosing the actuator size for a particular application and for the parameterization of controllers. Next, the behavior of these spring actuators when subjected to force and strain under realistic conditions is discussed based on the phase transformation temperatures and the actuator response to heating. A 3D wing prototype was tested in a wind tunnel under different air flows, showing the suitability of the actuators for this application. An adaptive wing prototype was constructed the variation in camber deflection is the response of actuator heating by the Joule effect.

The actuators work in a regime where the shape memory effect is created by heating of the stress-induced martensite phase, a phenomenon little explored in the literature. This work presents a thermomechanical characterization of NiTi SMA micro-springs for application in morphing wings. Particularly shape memory alloys (SMAs) have been investigated due to their ability to recover large deformations if subjected to a suitable temperature (simple drive mechanism by Joule heating). Some researchers have proposed the application of intelligent materials as alternative to conventional drive systems. This technology still has some limitations, among them the control mechanism of the shape adaptation mechanism. This concept aims to increase the flight efficiency of the aircraft by adapting the wing to the present air flow condition. The incessant quest for more efficient aircraft has driven research into the development of aircraft with morphing wings.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
